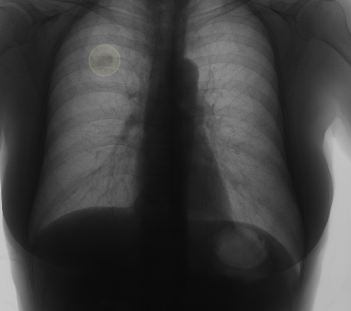
This is a data parser to obtain images and descriptions from JSRT database in a uniform format for deep learning applications.
The currently completed dataset augmentation part can increase dataset from 247 images to more than 2000 images by horizontal reflection, rotation by any degree, zooming to any location.
The attempted idea and possible implementation methods are mentioned here:
https://github.com/harishanand95/jsrt-parser/blob/master/Implementation_Idea_paper.pdf
This is an on-going project I'm working on. I have been busy lately. Contributions are welcome. I see this project as more of opensource application of an idea than a paper.
Update: Completed dataset augmentation part. It can specifically increase dataset from 247 images to more than 2000 images by horizontal reflection, rotation by any degree, zooming to any location.
Expected features:
-
Image transformations to increase the dataset size:
The training and validation sets will be augmented by applying a number of image transformations:
-
Horizontal reflection
jsrtdata = Jsrt().load_images("./All247images/") nodule_images = jsrtdata.get_images(num_of_images=3, has_nodule=True) # reflects only a single image nodule_images[0].horizontal_reflection() nodule_images[0].display() # reflects a list of images present in `nodule_images`. jsrtdata.horizontally_reflect_images(nodule_images) # reflects all the loaded images and increases the dataset. jsrtdata.augment_images(horizontal_reflection=True, rotate=False) -
Rotation by 2°-10°
jsrtdata = Jsrt().load_images("./All247images/") nodule_images = jsrtdata.get_images(num_of_images=3, has_nodule=True) # rotates a single image by 2° nodule_images[0].rotate(2) nodule_images[0].display() # rotates a list of images in `nodule_images` by 2° and 3° jsrtdata.rotate_image(nodule_images, [2, 3]) # rotates all the loaded images by 2° and 3°, and increases the dataset. jsrtdata.augment_images(horizontal_reflection=False, rotate=True, rotate_angles=[1, 2]) -
Translation of 3 pixels in cardinal or ordinal directions (Optional: not sure of its consequence to image)
-
Pixel spread (swap each pixel with a random adjacent pixel)
-
Noise reduction (replace each pixel with the value just before or after the median value in a neighborhood of 2 or 5 pixels)
-
Random noise addition.
In total, each image can serve as the progenitor of 106 child images with the label inherited from the parent image.
-
This is an attempt to augment the images similar to the one mentioned in High-Throughput Classification of Radiographs Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks by Alvin Rajkomar & Sneha Lingam & Andrew G. Taylor & Michael Blum & John Mongan.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10278-016-9914-9
-
Get random X type of images or just a random mix of images from the dataset.
-
Get image description and other attributes associated with each image.
img = JsrtImage() img.load_from_file("./All247images/JPCNN010.IMG") img.add_description(['JPCNN010.IMG', '54', 'male', 'non-nodule'], has_nodule=False) print img.image_type print img.image_width print img.image_height -
Display image with a marking over the location of the lung nodule.
img.display() -
Implement a method to find the new location of the nodule during an image's rotation.
-
Implement a method to find the new location of the nodule during an image's horizontal flip.
-
Option to load and save the images into a binary format.
jsrtdata = Jsrt().load_images("./All247images/") save_pic = jsrtdata.get_images(num_of_images=1) # write image to test.tfrecords jsrtdata.save_images(save_pic, "test.tfrecords") # read image from test.tfrecords read_pic = jsrtdata.read_images("test.tfrecords") # compare of saved image and read image print np.allclose(save_pic[0].image, read_pic[0].image) if save_pic[0].image_height == read_pic[0].image_height: print "True" if save_pic[0].image_width == read_pic[0].image_width: print "True" if save_pic[0].x == read_pic[0].x: print "True" if save_pic[0].y == read_pic[0].y: print "True" # You should get 5 True statement as results, which confirms that the values are same. -
Separate out test dataset from train and validation set.
-
(Optional) Implement a method to get a zoomed portion of the image given the coordinates to zoom and image size. Required for attention based models.
-
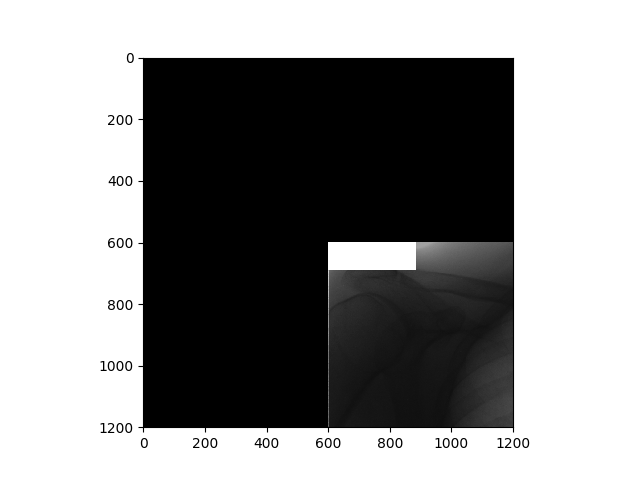
Implement a method to obtain the cropped image at a given location of any size from the image.
jsrtdata = Jsrt().load_images("./All247images/") nodule_images = jsrtdata.get_images(num_of_images=1, has_nodule=True) # crop out from image a picture of size 1200 at location 0,0 as center. image = nodule_images[0].crop(1200, 0, 0) plt.imshow(image, cmap=plt.get_cmap('gray')) plt.show() -
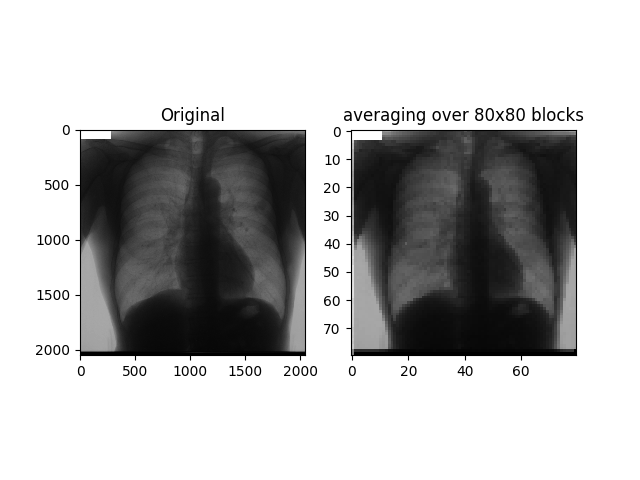
Downsampling of image.
This is necessary as some CNN architectures (like inception) expects inputs in fixed (like 299x299) size.
jsrtdata = Jsrt().load_images("./All247images/") nodule_images = jsrtdata.get_images(num_of_images=3, has_nodule=True) plt.subplot(121) plt.title("Original") plt.imshow(nodule_images[0].image, cmap=plt.get_cmap('gray')) plt.imshow(image, cmap=plt.get_cmap('gray')) plt.subplot(122) plt.title("averaging over 80x80 blocks") image = nodule_images[0].down_sample(1 / 25.6) plt.show()