pyCirclize is a circular visualization python package implemented based on matplotlib. This package is developed for the purpose of easily and beautifully plotting circular figure such as Circos Plot and Chord Diagram in Python. In addition, useful genome and phylogenetic tree visualization methods for the bioinformatics field are also implemented. pyCirclize was inspired by circlize and pyCircos. More detailed documentation is available here.
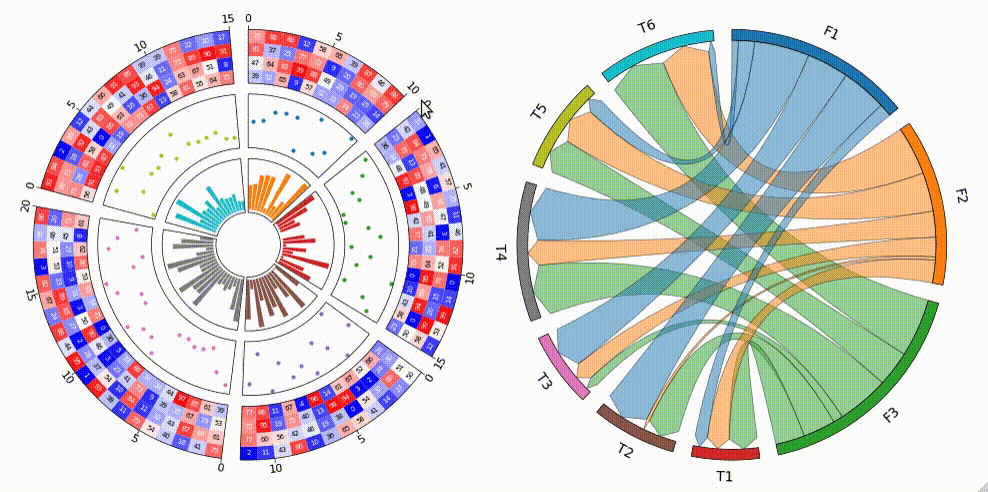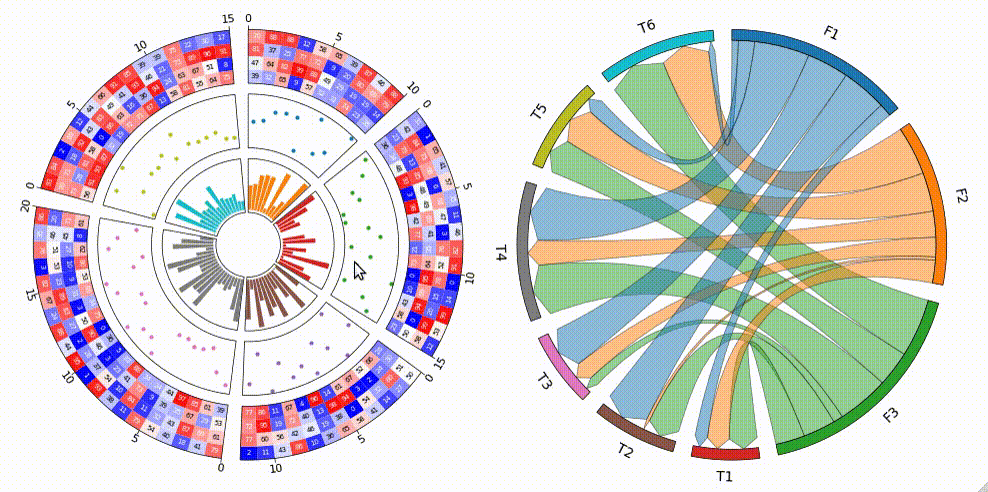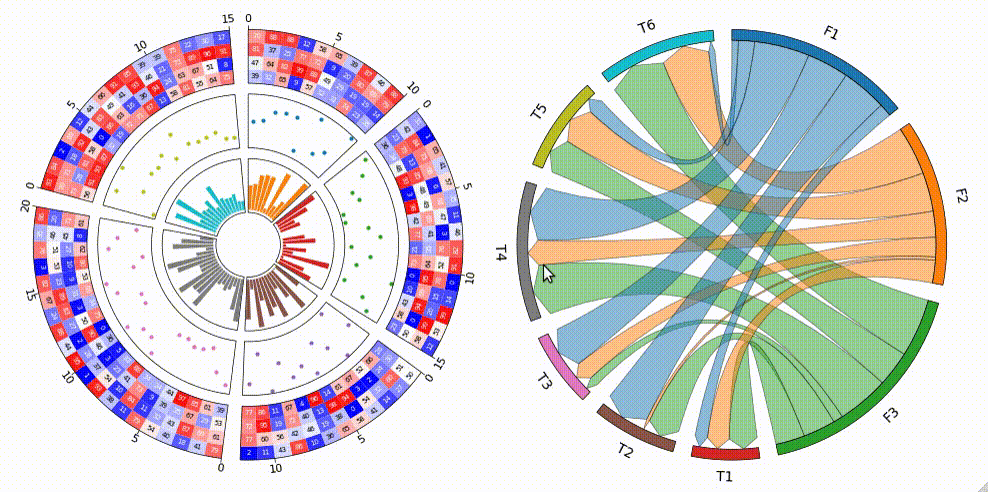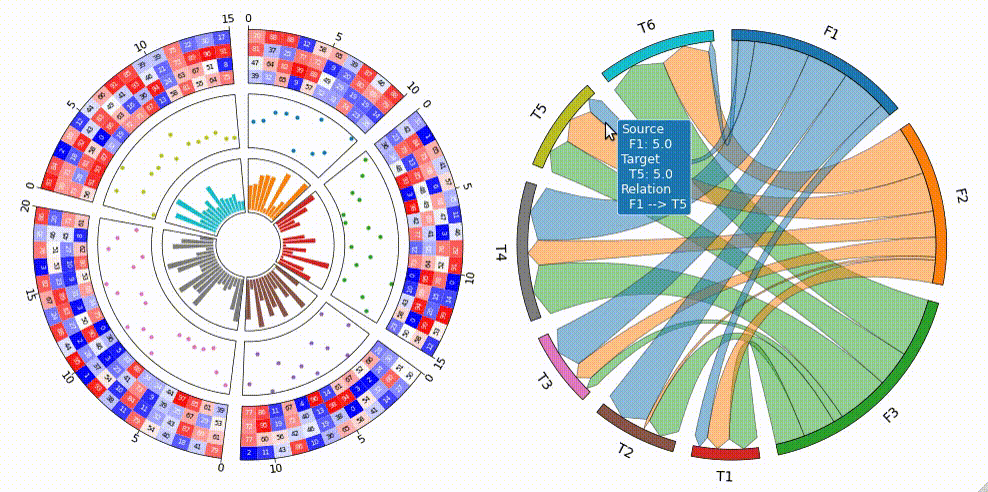
Fig.1 pyCirclize example plot gallery
Python 3.10 or later is required for installation.
Install PyPI package:
pip install pycirclize
Install conda-forge package:
conda install -c conda-forge pycirclize
API usage is described in each of the following sections in the document.
- Getting Started
- Plot API Example
- Chord Diagram
- Radar Chart
- Circos Plot (Genomics)
- Comparative Genomics
- Phylogenetic Tree
- Plot Tips
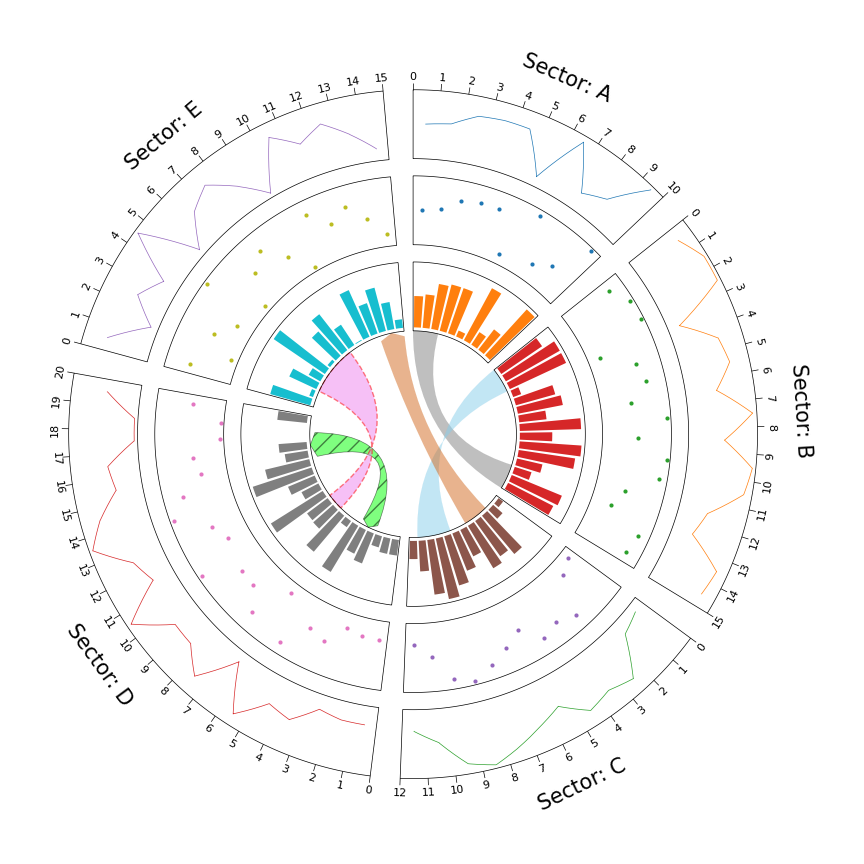
from pycirclize import Circos
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(0)
# Initialize Circos sectors
sectors = {"A": 10, "B": 15, "C": 12, "D": 20, "E": 15}
circos = Circos(sectors, space=5)
for sector in circos.sectors:
# Plot sector name
sector.text(f"Sector: {sector.name}", r=110, size=15)
# Create x positions & random y values
x = np.arange(sector.start, sector.end) + 0.5
y = np.random.randint(0, 100, len(x))
# Plot lines
track1 = sector.add_track((80, 100), r_pad_ratio=0.1)
track1.xticks_by_interval(interval=1)
track1.axis()
track1.line(x, y)
# Plot points
track2 = sector.add_track((55, 75), r_pad_ratio=0.1)
track2.axis()
track2.scatter(x, y)
# Plot bars
track3 = sector.add_track((30, 50), r_pad_ratio=0.1)
track3.axis()
track3.bar(x, y)
# Plot links
circos.link(("A", 0, 3), ("B", 15, 12))
circos.link(("B", 0, 3), ("C", 7, 11), color="skyblue")
circos.link(("C", 2, 5), ("E", 15, 12), color="chocolate", direction=1)
circos.link(("D", 3, 5), ("D", 18, 15), color="lime", ec="black", lw=0.5, hatch="//", direction=2)
circos.link(("D", 8, 10), ("E", 2, 8), color="violet", ec="red", lw=1.0, ls="dashed")
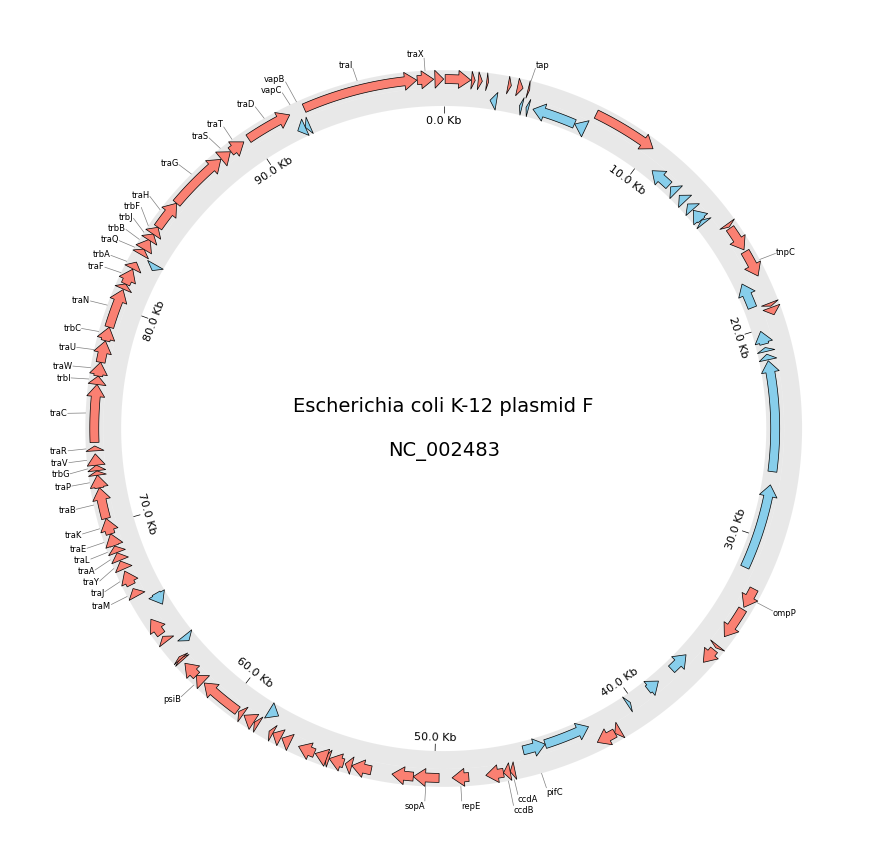
circos.savefig("example01.png")from pycirclize import Circos
from pycirclize.utils import fetch_genbank_by_accid
from pycirclize.parser import Genbank
# Download `NC_002483` E.coli plasmid genbank
gbk_fetch_data = fetch_genbank_by_accid("NC_002483")
gbk = Genbank(gbk_fetch_data)
# Initialize Circos instance with genome size
sectors = gbk.get_seqid2size()
space = 0 if len(sectors) == 1 else 2
circos = Circos(sectors, space=space)
circos.text(f"Escherichia coli K-12 plasmid F\n\n{gbk.name}", size=14)
seqid2features = gbk.get_seqid2features(feature_type="CDS")
for sector in circos.sectors:
# Setup track for features plot
f_cds_track = sector.add_track((95, 100))
f_cds_track.axis(fc="lightgrey", ec="none", alpha=0.5)
r_cds_track = sector.add_track((90, 95))
r_cds_track.axis(fc="lightgrey", ec="none", alpha=0.5)
# Plot forward/reverse strand CDS
features = seqid2features[sector.name]
for feature in features:
if feature.location.strand == 1:
f_cds_track.genomic_features(feature, plotstyle="arrow", fc="salmon", lw=0.5)
else:
r_cds_track.genomic_features(feature, plotstyle="arrow", fc="skyblue", lw=0.5)
# Plot 'gene' qualifier label if exists
labels, label_pos_list = [], []
for feature in features:
start = int(feature.location.start)
end = int(feature.location.end)
label_pos = (start + end) / 2
gene_name = feature.qualifiers.get("gene", [None])[0]
if gene_name is not None:
labels.append(gene_name)
label_pos_list.append(label_pos)
f_cds_track.annotate(label_pos, gene_name, label_size=6)
# Plot xticks (interval = 10 Kb)
r_cds_track.xticks_by_interval(
10000, outer=False, label_formatter=lambda v: f"{v/1000:.1f} Kb"
)
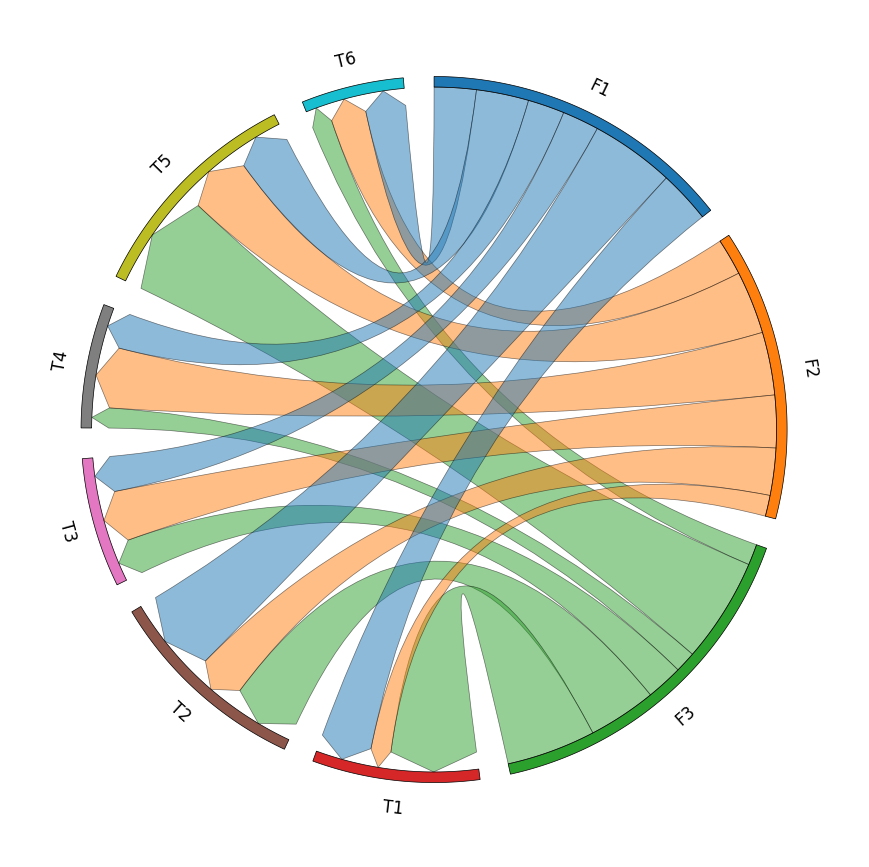
circos.savefig("example02.png")from pycirclize import Circos
import pandas as pd
# Create matrix dataframe (3 x 6)
row_names = ["F1", "F2", "F3"]
col_names = ["T1", "T2", "T3", "T4", "T5", "T6"]
matrix_data = [
[10, 16, 7, 7, 10, 8],
[4, 9, 10, 12, 12, 7],
[17, 13, 7, 4, 20, 4],
]
matrix_df = pd.DataFrame(matrix_data, index=row_names, columns=col_names)
# Initialize Circos instance for chord diagram plot
circos = Circos.chord_diagram(
matrix_df,
space=5,
cmap="tab10",
label_kws=dict(size=12),
link_kws=dict(ec="black", lw=0.5, direction=1),
)
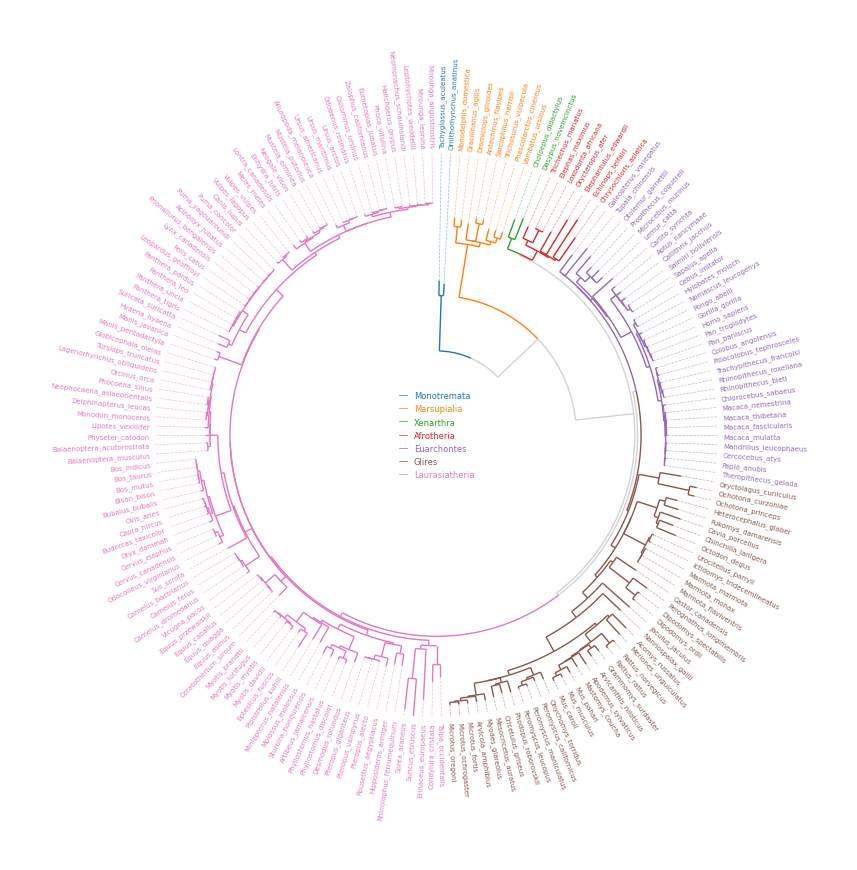
circos.savefig("example03.png")from pycirclize import Circos
from pycirclize.utils import load_example_tree_file, ColorCycler
from matplotlib.lines import Line2D
# Initialize Circos from phylogenetic tree
tree_file = load_example_tree_file("large_example.nwk")
circos, tv = Circos.initialize_from_tree(
tree_file,
r_lim=(30, 100),
leaf_label_size=5,
line_kws=dict(color="lightgrey", lw=1.0),
)
# Define group-species dict for tree annotation
# In this example, set minimum species list to specify group's MRCA node
group_name2species_list = dict(
Monotremata=["Tachyglossus_aculeatus", "Ornithorhynchus_anatinus"],
Marsupialia=["Monodelphis_domestica", "Vombatus_ursinus"],
Xenarthra=["Choloepus_didactylus", "Dasypus_novemcinctus"],
Afrotheria=["Trichechus_manatus", "Chrysochloris_asiatica"],
Euarchontes=["Galeopterus_variegatus", "Theropithecus_gelada"],
Glires=["Oryctolagus_cuniculus", "Microtus_oregoni"],
Laurasiatheria=["Talpa_occidentalis", "Mirounga_leonina"],
)
# Set tree line color & label color
ColorCycler.set_cmap("tab10")
group_name2color = {name: ColorCycler() for name in group_name2species_list.keys()}
for group_name, species_list in group_name2species_list.items():
color = group_name2color[group_name]
tv.set_node_line_props(species_list, color=color, apply_label_color=True)
# Plot figure & set legend on center
fig = circos.plotfig()
_ = circos.ax.legend(
handles=[Line2D([], [], label=n, color=c) for n, c in group_name2color.items()],
labelcolor=group_name2color.values(),
fontsize=6,
loc="center",
bbox_to_anchor=(0.5, 0.5),
)
fig.savefig("example04.png")from pycirclize import Circos
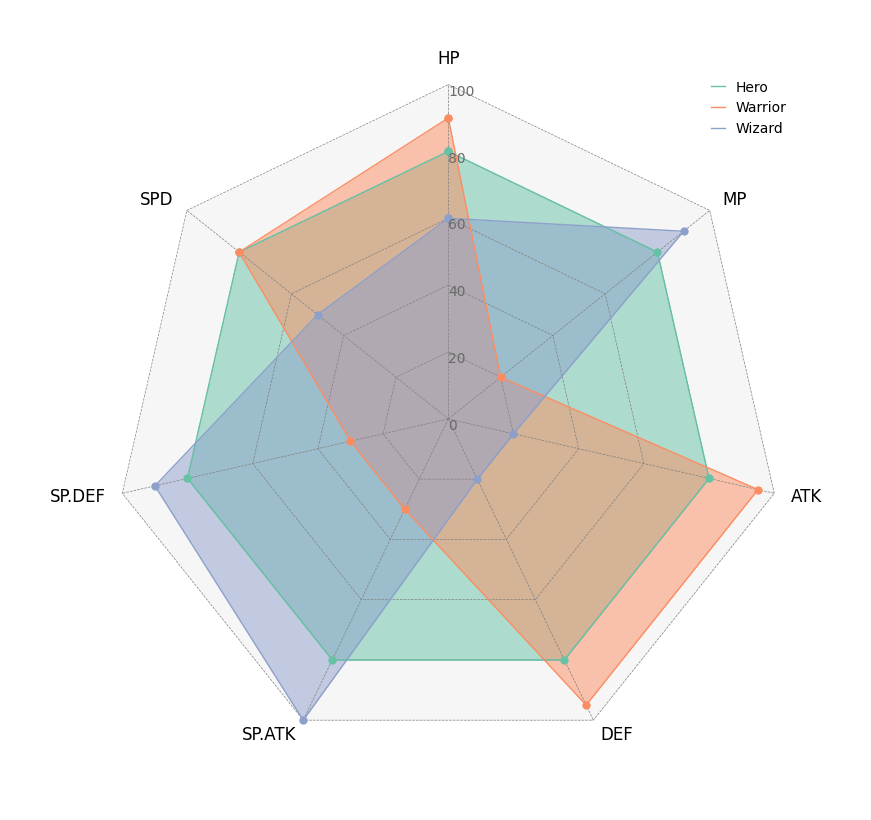
import pandas as pd
# Create RPG jobs parameter dataframe (3 jobs, 7 parameters)
df = pd.DataFrame(
data=[
[80, 80, 80, 80, 80, 80, 80],
[90, 20, 95, 95, 30, 30, 80],
[60, 90, 20, 20, 100, 90, 50],
],
index=["Hero", "Warrior", "Wizard"],
columns=["HP", "MP", "ATK", "DEF", "SP.ATK", "SP.DEF", "SPD"],
)
# Initialize Circos instance for radar chart plot
circos = Circos.radar_chart(
df,
vmax=100,
marker_size=6,
grid_interval_ratio=0.2,
)
# Plot figure & set legend on upper right
fig = circos.plotfig()
_ = circos.ax.legend(loc="upper right", fontsize=10)
fig.savefig("example05.png")pyCirclize supports tooltip display in jupyter using ipympl.
To enable tooltip, install pycirclize with ipympl and call circos.plotfig(tooltip=True) method.
Tooltip option is tested on jupyter notebooks in VScode and JupyterLab.
pip install pycirclize[tooltip]
# or
conda install -c conda-forge pycirclize ipymplWarning
Interactive tooltip plots require live python kernel. Be aware that tooltips are not always enabled in the notebook after plotting.