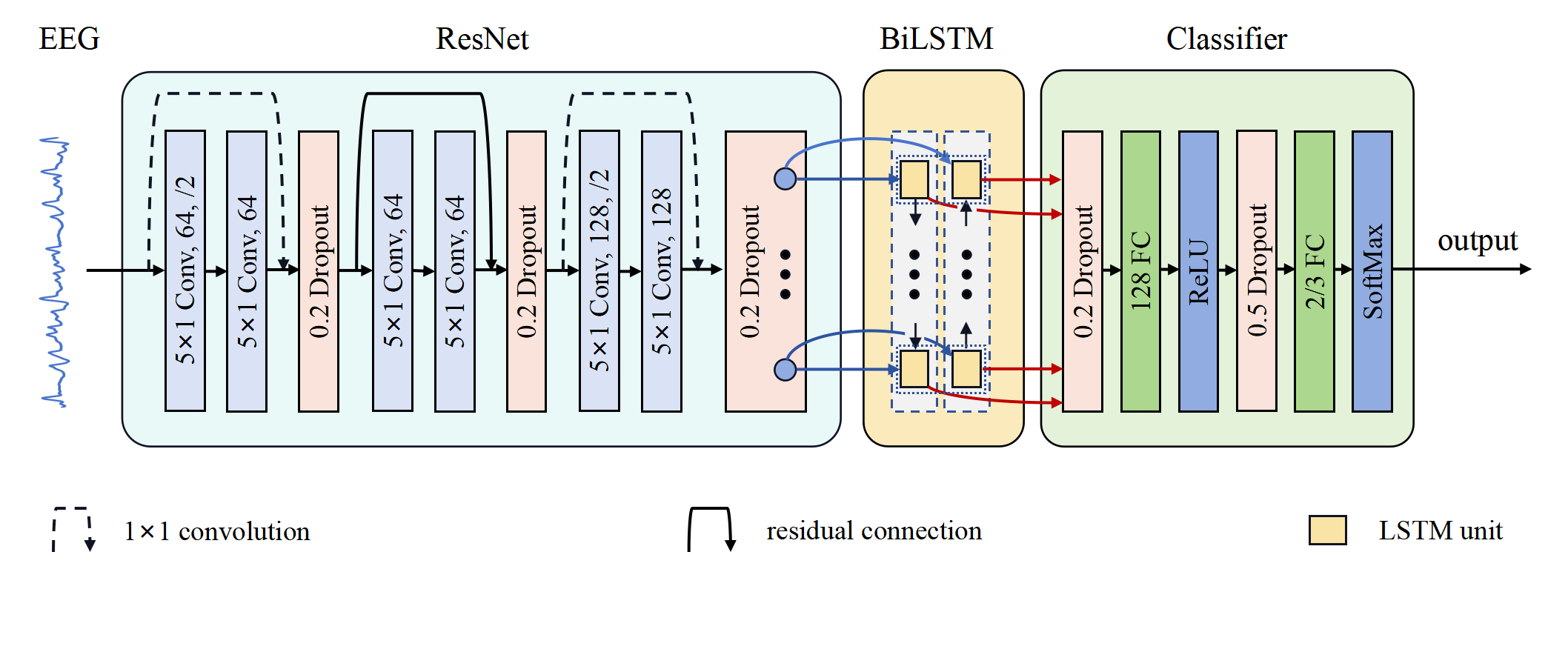
Electroencephalogram (EEG) plays a pivotal role in the detection and analysis of epileptic seizures, which affects over 70 million people in the world. Nonetheless, the visual interpretation of EEG signals for epilepsy detection is laborious and time-consuming. To tackle this open challenge, we introduce a straightforward yet efficient hybrid deep learning approach, named ResBiLSTM, for detecting epileptic seizures using EEG signals. Firstly, a one-dimensional residual neural network (ResNet) is tailored to adeptly extract the local spatial features of EEG signals. Subsequently, the acquired features are input into a bidirectional long short-term memory (BiLSTM) layer to model temporal dependencies. These output features are further processed through two fully connected layers to achieve the final epileptic seizure detection. The performance of ResBiLSTM is assessed on the epileptic seizure datasets provided by the University of Bonn and Temple University Hospital (TUH). The ResBiLSTM model achieves epileptic seizure detection accuracy rates of 98.88–100% in binary and ternary classifications on the Bonn dataset. Experimental outcomes for seizure recognition across seven epilepsy seizure types on the TUH seizure corpus (TUSZ) dataset indicate that the ResBiLSTM model attains a classification accuracy of 95.03% and a weighted F1 score of 95.03% with 10-fold cross-validation. These findings illustrate that ResBiLSTM outperforms several recent deep learning state-of-the-art approaches.
The TUSZ dataset stands as one of the largest and most well-acknowledged open-source epilepsy EEG datasets available to researchers, offering detailed clinical case descriptions. It includes annotations on the timing and types of epileptic seizures, as well as comprehensive patient information such as sex, age, medications, clinical history, seizure event count, and duration. Our study utilized the May 2020 release of the corpus (V1.5.2), comprising 3050 seizure cases across eight distinct seizure types, recorded at various sampling frequencies and montages. The seizure types include Focal Non-Specific Seizure (FNSZ), Generalized Non-Specific Seizure (GNSZ), Absence Seizure (ABSZ), Complex Partial Seizure (CPSZ), Tonic Clonic Seizure (TCSZ), Tonic Seizure (TNSZ), Simple Partial Seizure (SPSZ), and Myoclonic Seizure (MYSZ), as detailed in Table 1. Due to the limited number of MYSZ events, we excluded this type and focused on the remaining seven seizure categories for analysis.
Hope this code can be useful. I would appreciate you citing us in your paper. 😊
Zhao W, Wang W-F, Patnaik LM, Zhang B-C, Weng S-J, Xiao S-X, Wei D-Z and Zhou H-F (2024) Residual and bidirectional LSTM for epileptic seizure detection. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 18:1415967. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2024.1415967
QQ discussion group (Motor imagery, seizure detection, and seizure type classification [TUSZ]): 837800443
Email: zhaowei701@163.com