-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 23
[Before 2024] How to launch course tutorials
Our course tutorials are available as docker images with pre-installed software and data. There are two interfaces you can launch and work with the exercises: JupyterLab or command terminal.
You will be provided with the username and address to connect to a cloud server for running the exercises. To get on the server, you need to open up a shell command terminal on your computer and use ssh to connect to the server.
On MacOS and Linux, this is done using the terminal program and running
ssh student_##@agm#.statgen.us
where the # are the numbers provided to you for your account. After running this command, you'll be prompted for your password.
On Windows, using putty, connect to the host agm#.statgen.us, again where # have been provided; when you connect, you will then be prompted for your username and then your password.
You will then land in a shell environment ready to launch the exercises.
You can run the exercise either through JuptyerLab or through a command interface. Both options are discussed below. We recommend Option 1 when possible, but you can use Option 2 as plan B if the JupyterLab interface does not work as expected (typically due to low available memory in the cloud server).
We use docker to configure the tutorial software environment, and a script called statgen-setup, written in SoS language to initialize the docker containers for running the tutorials. If you use your own computer, e.g. a Mac or Linux laptop, you need to install docker and SoS, as well as the statgen-setup script.
Instructions below are tested on Mac and Linux computers. Currently we do not offer support to running under Windows, although it will still work for a Windows running the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). Windows users can follow the WSL installation instructions to configure their Windows system, before returning to the installation instructions below.
To open up JupyterLab server on Windows, it is recommended that a modern web browser be used, eg Edge instead of Internet Explorer.
Please download the docker installer for your operating system, and follow the instructions from the download page to install Docker.
A few notes for Mac users:
- After Docker is installed, please click on the Docker icon (found in your
Applications) to turn on the Docker Engine. You will need to use your user account at https://hub.docker.com to login to your Docker client in order to access imaged released on dockerhub. If you do not have an account please register one and use it. - Every time you restart your machine you may need to restart Docker Engine manually if you would like to run the tutorials. You should see a whale-like icon on your task bar indicating that docker service is running on the background of your computer.
- To test if Docker is installed properly and is ready to use, please open up a command terminal (found in your
Applications) and typedocker run hello-world. You should see greeting messages output on the screen, indicating successful installation.
SoS requires Python 3. You may skip the next section on micromamba if:
- your computer already has Python 3 and has the
pipmodule installed with Python 3; or - you already have a
condapackage manager installed with Python 3, (eg,micromamba,anaconda,miniconda), have worked withcondain the past and knows how to install software fromconda-forge.
To install SoS, please open a command terminal on your computer. For Mac users please type "terminal" in your Application home page and click on the app that shows up.
For those who needs to install Python 3 from scratch, we suggest installing Python 3 and SoS through micromamba. To do so, copy and paste this line to your terminal:
"${SHELL}" <(curl -L micro.mamba.pm/install.sh)
Follow the prompts to install. After installation is complete, you need to open up a new terminal window for the installation to take effect. You can type in the command terminal micromamba -h to verify the installation. You should see some output which indicates that installation is successful.
Next you can type:
micromamba activate
to activate the base environment, and use
micromamba install pip
to install pip.
Notice: every time you open a new terminal you need to first type micromamba activate to load this base Python 3 environment installed by micromamba, which will allow you to install and run commands necessary to launch the course material, as you will find in the rest of the document.
If you have the pip module for Python 3 you can install SoS using should be available if you have installed micromamba or other equivalent software environment. To install SoS, please type in command terminal pip install sos to download the latest software and install it. To verify the installation please type sos -h you should see valid output showing the command interface of the sos program.
Please download this statgen-set script, save it to your computer with filename statgen-setup. Then please open your command terminal, use cd command to navigate to where the file is downloaded and saved to (on Mac OS it should be ~/Downloads by default), and run
chmod +x statgen-setup
to make this script executable. You should now be able to run this script in the command terminal as ./statgen-setup from the directory it is downloaded to. Please test it by typing ./statgen-setup -h to output the help information for this script.
You can also move this script to specific folders in your system (bash PATH) such that you will be able to run it simply as statgen-setup without having to type in the path e.g. ./. One possibility is to install it to where sos program is installed. To do so, first type which sos to see the path where sos is installed to. Then you can move statgen-setup script to that same path (either via mv command on the terminal, or cut and paste it through the file manager in your operating system).
This is the only option for exercises written in IPython Notebooks (although JupyterLab also offers shell terminals that you can use to run command based tutorials). Currently available tutorials based on Ipython Notebooks are:
finemapldpred2vatpseqregenie
To launch, for example finemap exercise in JupyterLab, run from the command terminal:
statgen-setup launch --tutorial finemap
Or, e.g., ~/Downloads/statgen-setup launch --tutorial finemap if statgen-setup script is located in ~/Dowlnoads and not is installed to the system's PATH (and thus cannot be accessed via simply running statgen-setup).
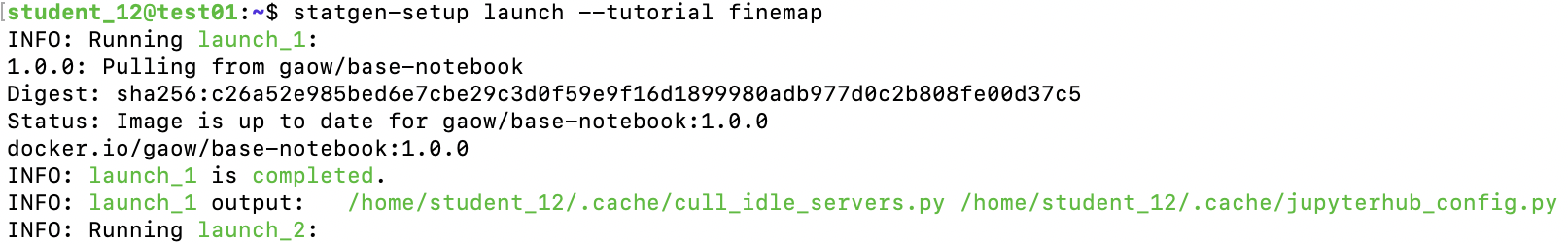
When it's done, you should see a line printed on the screen that contains a URL:
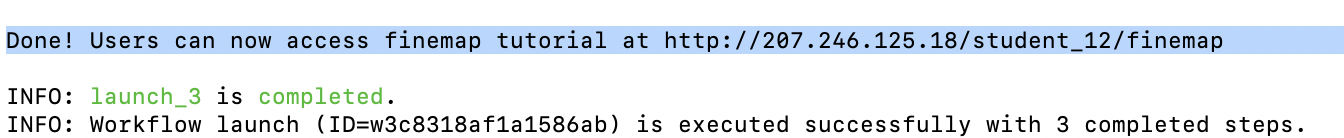
In this example it is http://207.246.125.18/student_12/finemap. Please copy that URL to your web browser. Your JupyterLab server should start like this:
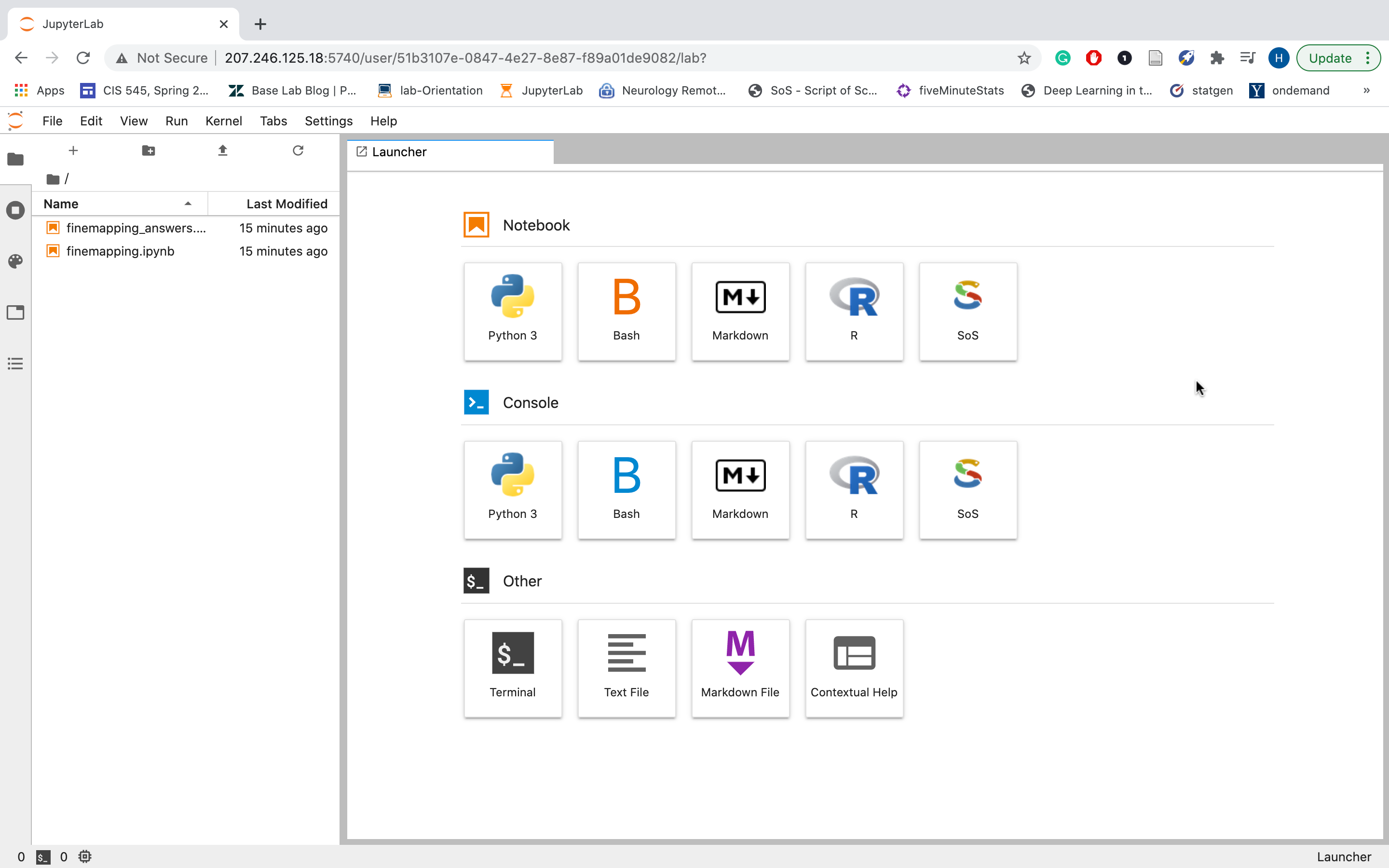
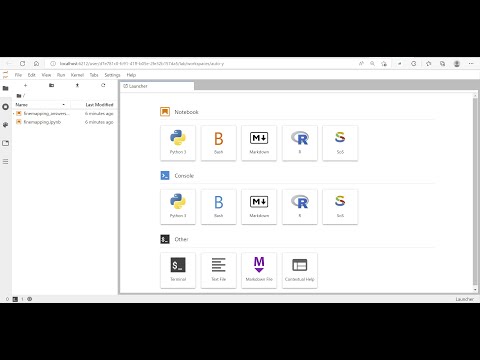
The left panel of the JupyterLab displays all files available. If you see IPython notebooks (.ipynb files) displayed, you can click on them to launch and run the tutorial directly from these notebooks. Otherwise, please click on the PDF documents (.pdf files) to show them in the browser, and follow the instructions to run them in the terminal console that you can launch from JupyterLab. In some tutorials you will see a README file that prompts you to open a terminal console from JupyterLab and run get-data to download and deploy the tutorial material. It may take a while for get-data command to load the data. Please wait to start the tutorials until after the command is complete.
How to launch terminal console from JupyterLab:
Click on File--> New --> Terminal
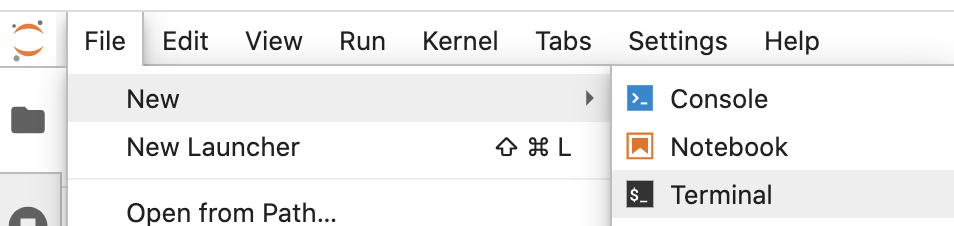
Then your Terminal console should be launched:
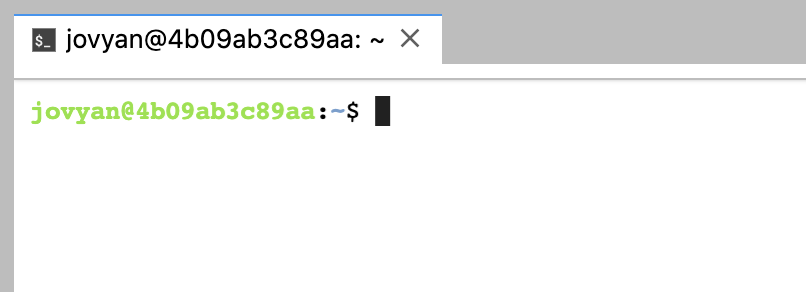
When running:
./statgen-setup launch --tutorial regenieIf you encounter this error:
INFO: Running launch_1:
INFO: launch_1 (index=0) is ignored due to saved signature
INFO: launch_1 output: /Users/rui/.cache/cull_idle_servers.py /Users/rui/.cache/jupyterhub_config.py
INFO: Running launch_2:
[+] Building 0.0s (2/2) FINISHED
=> ERROR [internal] load build definition from tmp3oh4c6y2.sh 0.0s
=> => transferring dockerfile: 105B 0.0s
=> [internal] load .dockerignore 0.0s
=> => transferring context: 2B 0.0s
------
> [internal] load build definition from tmp3oh4c6y2.sh:
------
failed to solve with frontend dockerfile.v0: failed to read dockerfile: error from sender: open /private/var/folders/1h/_nt0sxws2rj37y_w2tpb44y80000gq/T/TemporaryItems: operation not permitted
ERROR: launch_2 (id=cc97711143d7f614) returns an error.
ERROR: [launch_2]: [0]:
Failed to execute docker build . --tag regenie_rui -f /Users/rui/.sos/eb839d5e4ef45b46/launch_2_0_38f1fc07.sh
exitcode=1, workdir=/Users/rui/.cache
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
[launch]: Exits with 1 pending step (launch_3)
Solution: (reference) Open your terminal and run:
export DOCKER_BUILDKIT=0
export COMPOSE_DOCKER_CLI_BUILD=0We have the server configured to make it possible to export a notebook as docx file (MS Word format)
to your local computer. To do this, simply click on File button as shown above, then Export Notebook As -> Export Notebook to Docx. Notice that PDF format export is
currently not supported (requires xelatex which we don't install in our server).
We terminate the JupyterLab container instances periodically to maintain the cloud server at a reasonable load. Currently this is configured to happen daily at midnight. The files generated from the tutorials will still be saved to the hard drive, but data in the memory will be lost. This includes the bash environments and R variables for relevant exercises. You can always resume your previous analysis with a new container instance, but you'll have to reset some of these variables. For example for ldpred2 exercise, the variable:
work_dir="height_results"
at the beginning of the exercise needs to be reset every time the JupyterLab instance restarts.
In addition to tutorials available from JupyterLab as described above, the following tutorials are available from command terminal:
annovarepistasisfastlmm-gctageminiplinkmlinkpleiotropynpspopgenregressionslink
To run, for example finemap exercise from command terminal, please run:
statgen-setup login --tutorial finemap
You will be in a command environment. Please navigate to work directory by typing
cd work

If you do not see data files under this directory, that means the data is too large to warrant preloading them to the docker image. Please run get-data command to download them (it may take a while). You can then start working on the tutorials now by copy-paste text from handouts (PDF, HTML or Ipython notebook format), or by typing in the commands directly.
When you are done with the tutorial just type exit to exit. If you log in again, your session should resume unless the container has been terminated externally. If you want to fresh restart the container you can add --restart switch to the command above.
Notice that work folder is mounted to the physical hard drive of the computer system as a folder under your HOME directory. Only the files under this work folder will be saved to your computer. Files outside work will be temporarily saved to the docker container instance and will be lost if you terminate or restart the docker container.
If you share a Linux account with other students, you need to add --my-name to the launch commands:
statgen-setup launch --tutorial <tutorial> --my-name <my-name>
statgen-setup login --tutorial <tutorial> --my-name <my-name>
where <tutorial> is one of the available tutorials. <my-name> is any (unique) identification of your choice that should not conflict with the choice of another user if you share a computer. If you have your unique Linux user accounts, you can leave it unspecified.
To facilitate users setting up their computer for the course exercises, we have prepared video instructions available on YouTube.
Please open a ticket in our issue tracker if you have any difficulty setting up your system: https://github.com/statgenetics/statgen-courses/issues We will help you trouble-shoot.