A Python library for signal decomposition algorithms 🥳
Installation | Example Script | Target | Acknowledgements
You can install PySDKit through pip:
pip install pysdkit
We only used NumPy, Scipy and matplotlib when developing the project.
This project integrates simple signal processing methods, signal decomposition and visualization, and builds a general interface similar to Scikit-learn. It is mainly divided into three steps:
- Import the signal decomposition method;
- Create an instance for signal decomposition;
- Use the
fit_transformmethod to implement signal decomposition; - Visualize and analyze the original signal and the intrinsic mode functions IMFs obtained by decomposition.
from pysdkit import EMD
from pysdkit.data import test_emd
from pysdkit.plot import plot_IMFs
t, signal = test_emd()
# create an instance for signal decomposition
emd = EMD()
# implement signal decomposition
IMFs = emd.fit_transform(signal, max_imfs=2)
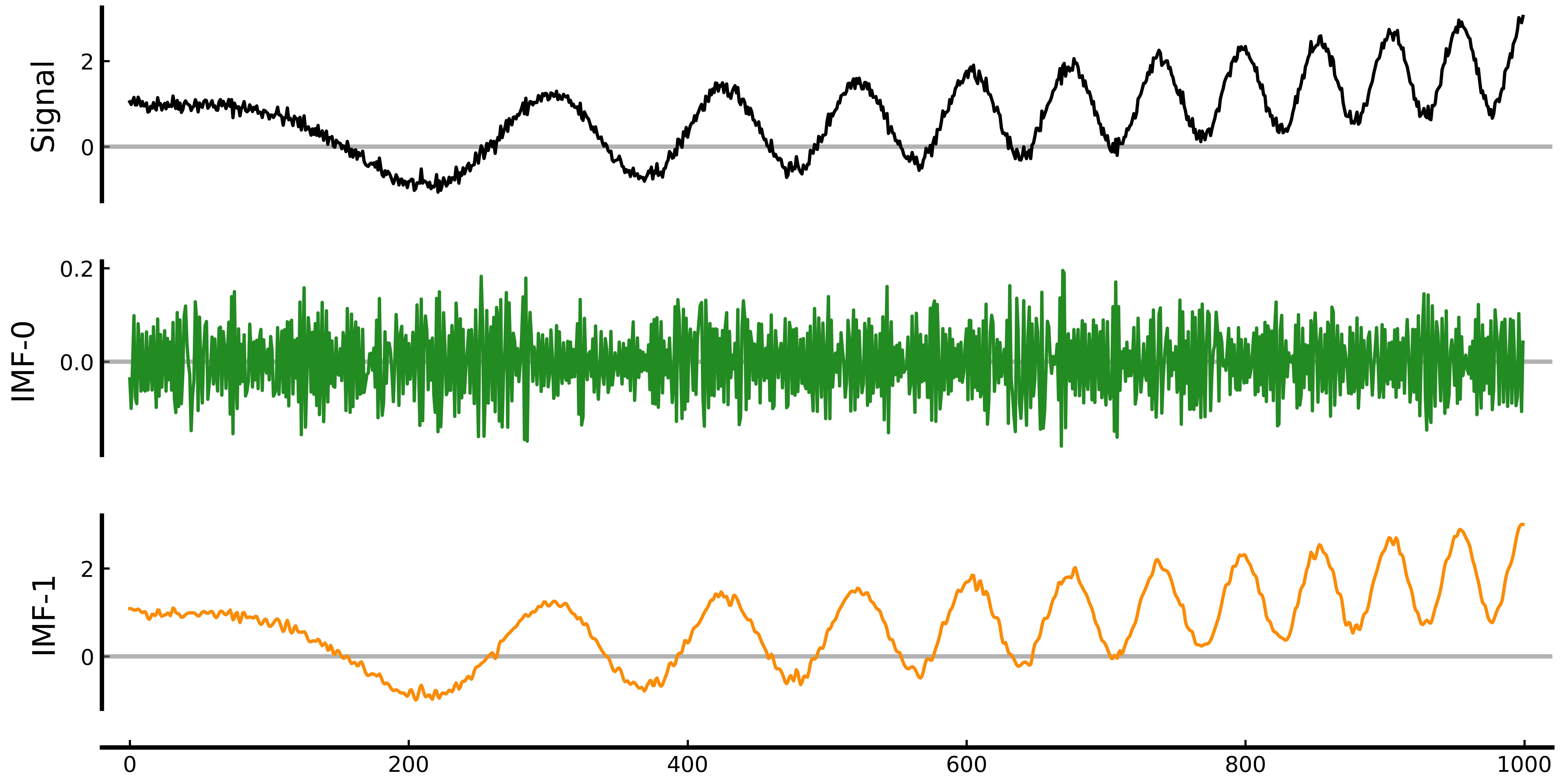
plot_IMFs(signal, IMFs)The EMD in the above example is the most classic empirical mode decomposition algorithm in signal decomposition. For more complex signals, you can try other algorithms such as variational mode decomposition (VMD).
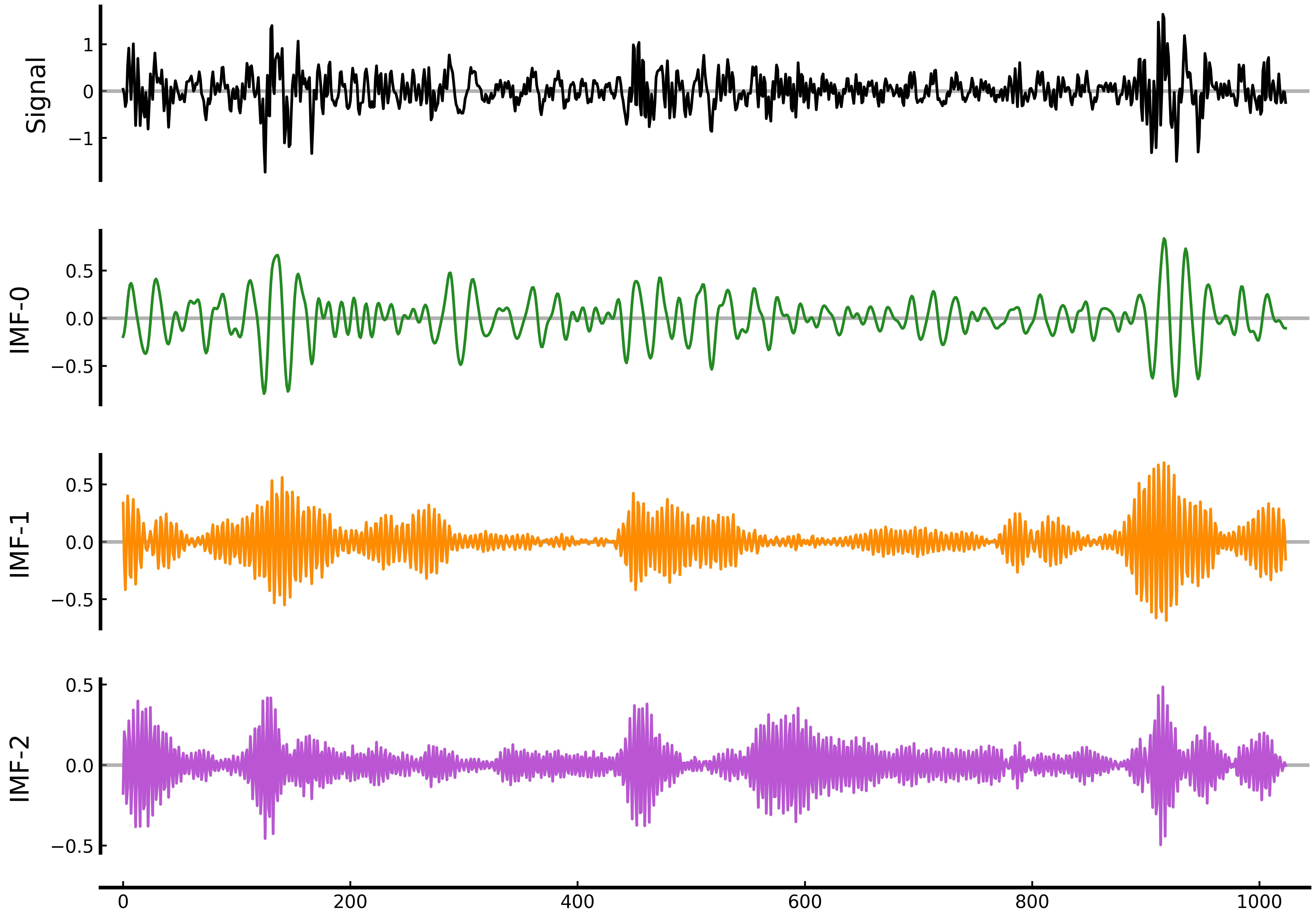
import numpy as np
from pysdkit import VMD
# load new signal
signal = np.load("./example/example.npy")
# use variational mode decomposition
vmd = VMD(alpha=500, K=3, tau=0.0, tol=1e-9)
IMFs = vmd.fit_transform(signal=signal)
print(IMFs.shape)
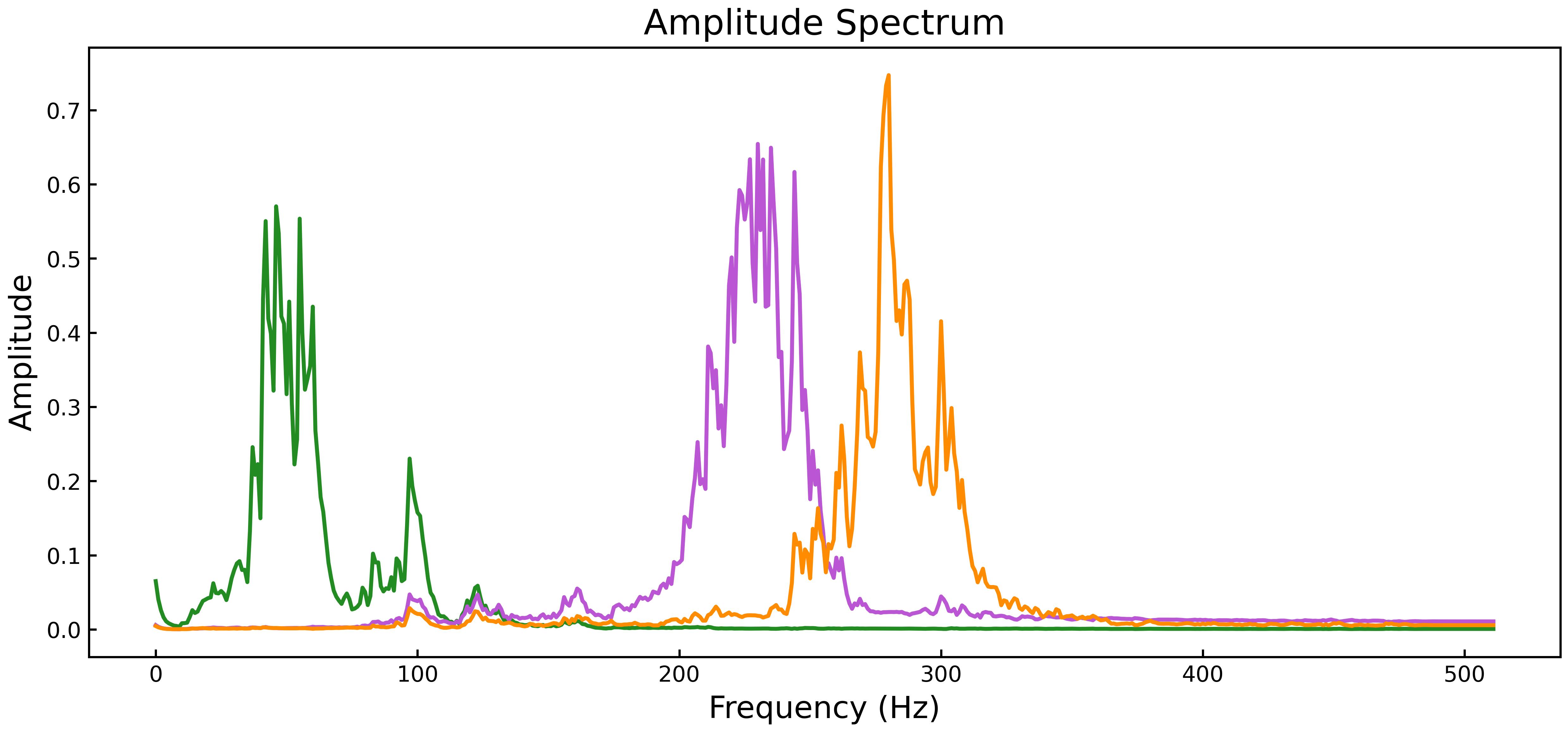
vmd.plot_IMFs(save_figure=True)Better observe the characteristics of the decomposed intrinsic mode function in the frequency domain.
from pysdkit.plot import plot_IMFs_amplitude_spectra
# frequency domain visualization
plot_IMFs_amplitude_spectra(IMFs, smooth="exp") # use exp smoothPySDKit is still under development. We are currently working on reproducing the signal decomposition algorithms in the table below, including not only common decomposition algorithms for univariate signals such as EMD and VMD, but also decomposition algorithms for multivariate signals such as MEMD and MVMD. We will also further reproduce the decomposition algorithms for two-dimensional images to make PySDKit not only suitable for signal processing, but also for image analysis and understanding. See Mission for the reasons why we developed PySDKit.
| Algorithm | Paper | Code | State |
|---|---|---|---|
EMD (Empirical Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
MEMD (Multivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
BEMD (Bidimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
CEMD (Complex Empirical Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
EEMD (Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
REMD (Robust Empirical Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
EMD2D (Empirical Mode Decomposition 2D for images) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
BMEMD (Bidimensional Multivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
CEEMDAN (Complete Ensemble EMD with Adaptive Noise) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
TVF_EMD (Time Varying Filter Based EMD) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
EFD (Empirical Fourier Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
FAEMD (Fast and Adaptive EMD) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
FAEMD2D (Two-Dimensional Fast and Adaptive EMD) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
FAEMD3D (Three-Dimensional Fast and Adaptive EMD) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
HVD (Hilbert Vibration Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
ITD (Intrinsic Time-Scale Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
ALIF (Adaptive Local Iterative Filtering) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
LMD (Local Mean Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
RLMD (Robust Local Mean Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
FMD (Feature Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
NFMD (Non-stationary Feature Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
SSA (Singular Spectral Analysis) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
EWT (Empirical Wavelet Transform) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
EWT2D (2D Empirical Wavelet Transform) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
VMD (Variational Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
MVMD (Multivariate Variational Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
VMD2D (Two-Dimensional Variational Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
CVMD2D (Two-Dimensional Compact Variational Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
VME (Variational Mode Extraction) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
SVMD (Successive Variational Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
VNCMD (Variational Nonlinear Chirp Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
INCMD (Iterative Nonlinear Chirp Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
MNCMD (Multivariate Nonlinear Chirp Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
AVNCMD (Adaptive Variational Nonlinear Chirp Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
ACMD (Adaptive Chirp Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
BA-ACMD (Bandwidth-aware adaptive chirp mode decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
JMD (Jump Plus AM-FM Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ️✔️ |
MJMD (Multivariate Jump Plus AM-FM Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
ESMD (Extreme-Point Symmetric Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
STNBMD (Short-Time Narrow-Band Mode Decomposition) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
STL (Seasonal-Trend decomposition using LOESS) |
[paper] | [code] | ✔️ |
MSTL (Multivariate Seasonal-Trend decomposition using LOESS) |
[paper] | [code] | ✖️ |
We would like to thank the researchers in signal processing for providing us with valuable algorithms and promoting the continuous progress in this field. However, since the main programming language used in signal processing is Matlab, and Python is the main battlefield of machine learning and deep learning, the usage of signal decomposition in machine learning and deep learning is far less extensive than wavelet transformation. In order to further promote the organic combination of signal decomposition and machine learning, we developed PySDKit. We would like to express our gratitude to PyEMD, Sktime, Scikit-learn, Scikit-Image, statsmodels, vmdpy, MEMD-Python-, ewtpy, EWT-Python, PyLMD, pywt, SP_Liband dsatools, signal-decomposition.